
Key Takeaways
-
Macular degeneration can be managed with specific vitamins and minerals based on the AREDS studies.
-
Lutein and zeaxanthin are critical antioxidants for eye health, helping to protect the macula.
-
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for maintaining cell structure and health in the retina.
-
Zinc plays a protective role in eye health and can help slow the progression of macular degeneration.
-
It’s important to choose high-quality supplements and combine them with a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and fish for the best defense against macular degeneration.
Spotlight on Macular Degeneration: A Senior’s Guide

“Reading using spectacles. | An 81-year …” from www.flickr.com and used with no modifications.
Macular degeneration isn’t just a term you hear at the doctor’s office—it’s a reality for millions of people, especially seniors. It’s a condition where the central part of the retina, called the macula, starts to deteriorate. This part of your eye is responsible for sharp, detailed vision. When it’s compromised, so is your ability to read, drive, and see fine details. But here’s the good news: you can take steps to manage it, and it starts with understanding what vitamins and minerals your eyes really need.
Understanding Macular Degeneration
Think of the macula as the high-definition part of your eye. It’s what you use when you’re focusing on something right in front of you. Macular degeneration happens when this tiny part of the retina starts to break down. There are two types: dry and wet. Dry is more common and less severe, while wet can lead to more serious vision loss.
Age is the biggest risk factor, but genetics, smoking, and high blood pressure can also up your chances. Symptoms include blurry vision, dark areas in your central vision, and colors that seem less bright. If you’re squinting to read this, it’s time to talk to your eye doctor.
Vital Vitamins to Curtail Progression
Let’s cut to the chase: certain vitamins and minerals can make a big difference. Based on landmark studies known as AREDS and AREDS2, we now know which nutrients can help slow the progression of macular degeneration. These studies were like the all-stars of eye health research, and they’ve given us a clear game plan.
Nutrients That Nurture Healthy Vision
So, what’s on the menu for healthy eyes? A few key nutrients stand out:
Powerhouse Antioxidants: Lutein and Zeaxanthin
These two are like the dynamic duo for your eyes. They’re found in high concentrations in the macula and act like natural sunglasses, filtering out harmful blue light and fighting off damage from the sun and screens. You can find them in leafy greens like spinach and kale, but for those with macular degeneration, supplements can provide a much-needed boost.
Because these antioxidants are so important, let’s break it down further:
-
Lutein and zeaxanthin help protect the eyes from oxidative stress, which can damage the macula.
-
They’re best absorbed with a meal that includes some fat, as they’re fat-soluble nutrients.
-
Aiming for about 10 mg of lutein and 2 mg of zeaxanthin per day is a good target, but always check with your doctor before starting any new supplement.
Essential Fatty Acids: Omega-3s Role in Eye Health
Omega-3 fatty acids are the building blocks of cell membranes, and they’re crucial for the health of your retina. DHA, a type of omega-3, is particularly important and is naturally found in the retina. Fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are great sources, but if fish isn’t your thing, a high-quality fish oil supplement can fill in the gaps.
Here’s why omega-3s are non-negotiable for your eyes:
-
They help maintain the integrity of the retinal cells.
-
Omega-3s have anti-inflammatory properties that can help with the overall health of your eyes.
-
Supplementing with fish oil can also benefit those who don’t get enough omega-3s in their diet.
Zinc: The Mineral Protector

“oysters on the half-shell – closeup …” from www.flickr.com and used with no modifications.
Zinc is like the bodyguard of your eye nutrients—it helps bring vitamin A from your liver to your retina to produce melanin, a protective pigment in the eyes. Oysters, beef, and pumpkin seeds are all rich in zinc, but if you’re not getting enough through diet alone, a supplement can be a smart move.
When it comes to zinc, remember:
-
It’s been shown to help slow the progression of macular degeneration when taken in the right amounts.
-
The AREDS studies recommend 40 to 80 mg of zinc per day, but it’s important not to overdo it as too much can have side effects.
-
Always balance zinc intake with copper, as high levels of zinc can deplete copper levels in the body.
The Age-Related Eye Disease Studies (AREDS and AREDS2) have been instrumental in shaping our approach to eye health, particularly for those with macular degeneration. The original AREDS study pinpointed a combination of vitamins C and E, beta-carotene, zinc, and copper as beneficial. AREDS2 went further, tweaking the formula by adding lutein and zeaxanthin and suggesting omega-3 fatty acids, while removing beta-carotene, which has been linked to increased risk of lung cancer in smokers.
Enhanced Benefits with AREDS2 Adjustments
The adjustments made in the AREDS2 study aren’t just minor changes; they’re significant improvements that cater to a wider range of individuals, especially considering the risks associated with beta-carotene. By focusing on lutein and zeaxanthin, the study acknowledges the critical role these nutrients play in eye health and provides a safer option for everyone, smoker or not.
Picking the Perfect Eye Vitamin
Choosing the right eye vitamin is crucial for managing macular degeneration. The market is flooded with options, and it can be overwhelming to decide which one is best for you. Here’s what you should keep in mind:
Finding the Right Formulation: What to Look for

When selecting an eye vitamin, aim for a product that aligns with the AREDS or AREDS2 recommendations. Look for the following:
-
A combination of antioxidants (vitamin C and E)
-
Lutein and zeaxanthin
-
Zinc and copper
-
Omega-3 fatty acids (specifically DHA and EPA)

“Omega 3 Images | Free Photos, PNG …” from www.rawpixel.com and used with no modifications.
These ingredients together create a powerful defense against the progression of macular degeneration. And remember, quality matters—choose reputable brands that have third-party testing for purity and potency.
Accessing the Supplements: Quality and Cost Considerations
Quality eye vitamins can be an investment in your health, but they don’t have to break the bank. Compare prices and check for certifications from organizations like NSF or USP. These certifications can give you peace of mind that what’s on the label is what’s in the bottle. Also, consider purchasing larger quantities or subscription services for discounts, but only after you’ve confirmed that a particular brand works for you.
Synergizing Diet with Supplements
While supplements are important, they’re just one piece of the puzzle. Combining them with the right diet can amplify their benefits.
Green Leafy Vegetables: A Sight-Saving Staple

“Paper bag with green leafy vegetables …” from www.flickr.com and used with no modifications.
Leafy greens like spinach, kale, and collard greens are loaded with lutein and zeaxanthin. These veggies should be a staple in your diet because they offer the antioxidants your eyes need in a form that’s easy for your body to use. Aim for at least one serving per day—more if you can manage it.
Fruits and Fish: Diversifying for Eye Health

“Fish) Sou… | Flickr” from www.flickr.com and used with no modifications.
Besides leafy greens, expand your diet to include a variety of colorful fruits and oily fish. Oranges, berries, and other fruits provide vitamin C, while fish like salmon and mackerel are rich in omega-3s. These foods offer a natural spectrum of nutrients that support overall eye health and complement your supplement regimen.
Implementing Lifestyle Changes for Better Vision
Supplements and diet are important, but lifestyle changes can further protect your vision. Simple steps like wearing sunglasses to block UV rays and taking breaks during screen time can make a big difference.
It’s also essential to manage other health conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure, as they can impact your eye health. Regular exercise, not smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight all contribute to healthier eyes.
Let’s dive deeper into a couple of these lifestyle changes:
Shielding Your Sight: The Impact of UV Protection

“Yellow Plastic Sunglasses | Everything …” from www.flickr.com and used with no modifications.
Too much exposure to UV light can worsen macular degeneration. Always wear sunglasses with 100% UVA and UVB protection when you’re outdoors, even on cloudy days. Wide-brimmed hats can also help shield your eyes from the sun.
Screen Time and Eye Strain: Finding the Balance
In today’s digital world, it’s hard to avoid screens, but they can strain your eyes. Follow the 20-20-20 rule: every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for at least 20 seconds. This simple habit can reduce eye strain and give your eyes a much-needed break.
Most importantly, don’t forget the value of regular eye exams. An eye care professional can detect early signs of macular degeneration and help you create a personalized plan to manage your eye health.
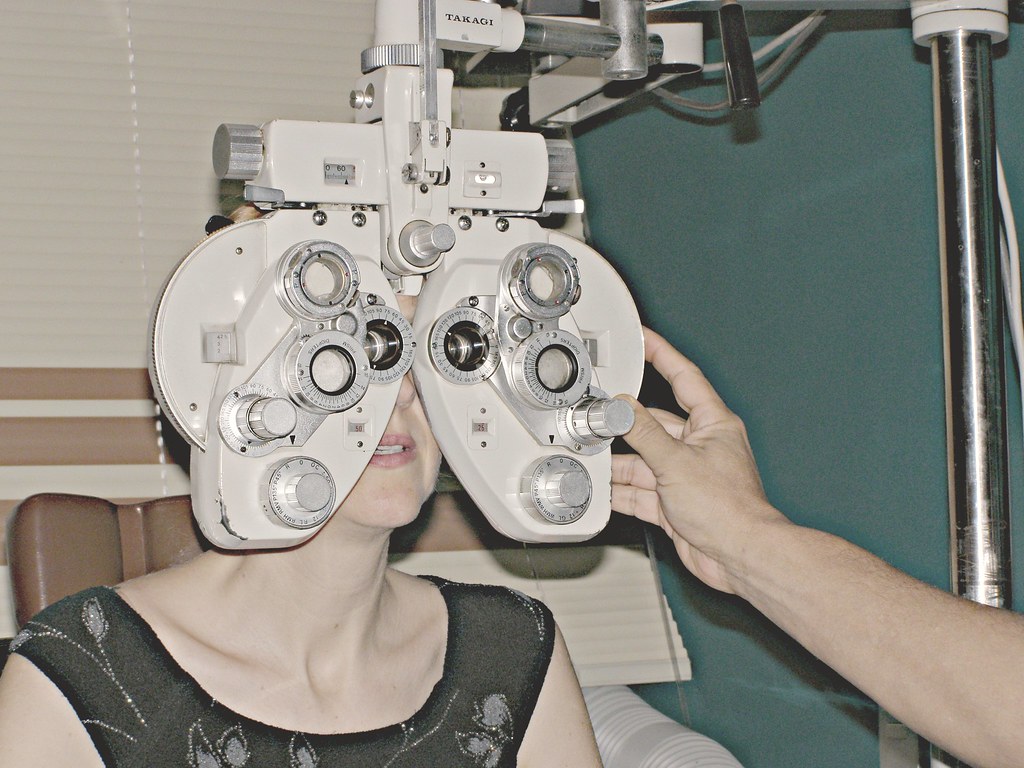
“ophthalmology | Medical examination of …” from www.flickr.com and used with no modifications.
Remember, every step you take towards a healthier lifestyle contributes to the health of your eyes. By combining the right supplements, diet, and lifestyle changes, you can maximize your chances of maintaining good vision well into your golden years.
When to Consult an Eye Care Professional
It’s crucial to keep in regular contact with an eye care professional, especially as you age. They can catch early signs of macular degeneration that you might miss. Remember, the earlier you catch it, the more you can do to manage it.
Recognizing the Signs of Macular Degeneration
Know the signs: if straight lines start to look wavy, or you notice blurry areas or whiteout spots in your central vision, these could be early symptoms of macular degeneration. Don’t wait to see if they’ll go away on their own. Make an appointment with your eye doctor right away.
Regular Screenings and Individualized Care Plans
Regular eye exams are non-negotiable. They’re the only way to detect changes in your vision that you might not notice. Your eye doctor can also work with you to develop a care plan that’s tailored to your needs, which might include supplements, diet changes, and lifestyle adjustments.
FAQs About Eye Health and Macular Degeneration
Let’s tackle some common questions about eye health and macular degeneration to clear up any confusion and provide you with the information you need.
Can Macular Degeneration be Reversed with Vitamins?
No, macular degeneration cannot be reversed with vitamins. However, specific vitamins and supplements based on the AREDS studies can help slow its progression. It’s about management, not cure.
How Often Should You Take Eye Vitamins?
Typically, you should take eye vitamins daily to align with the dosages recommended by the AREDS studies. But always consult with your eye doctor for advice tailored to your specific condition.
Are there Side Effects to Macular Degeneration Supplements?
Like any supplement, those designed for eye health can have side effects, especially if taken in excessive amounts. Stick to the recommended dosages, and consult with your doctor if you experience any unusual symptoms.
Can Lifestyle Changes Alone Improve Macular Degeneration?
While lifestyle changes alone cannot cure macular degeneration, they can certainly help manage it and may slow its progression. Think of lifestyle changes as part of a holistic approach to maintaining your eye health.
What is the Difference Between AREDS and AREDS2?
The main difference between AREDS and AREDS2 is the formula. AREDS2 replaced beta-carotene with lutein and zeaxanthin, added omega-3 fatty acids, and reduced zinc. This updated formula is considered safer and more effective for a broader range of individuals.


